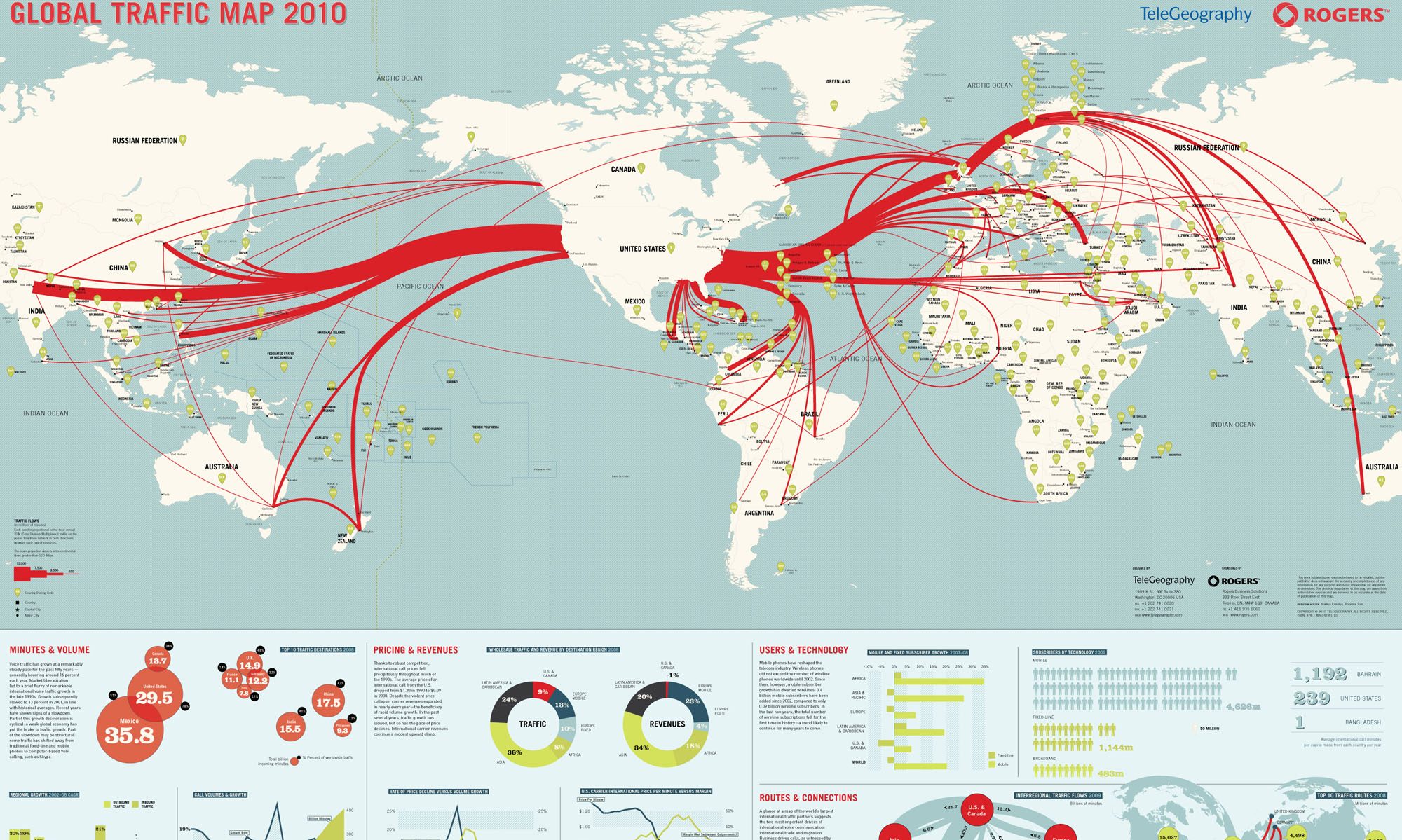
These are important words that we use in our InDesign classes. These words help students further understand the InDesign curriculum.
Character style – is a collection of formatting attributes that can be applied to text that already has a paragraph style applied to it.
Paragraph style – includes both characters and paragraph formatting attributes, and can be applied to a selected paragraph or range of paragraphs.
Object styles – includes settings for stroke, color, transparency, drop shadows, paragraph styles, text-wrap, and more; you can also assign different transparency effects for the object, fill, stroke, and text.
Hidden characters – these are non-printing characters that display spaces, tabs, ends of paragraphs, index markers, and ends of stories. These special characters are visible only in a document window on the screen and can be toggled on or off in the Type menu.
Overset symbol – is a red plus sign that indicates that there is more content than the frame can display.
Threading text – the process of creating linked text frames. This will allow the flow of text from one text frame to the next.
Emphasis – provides direction to various elements in a given design.
Focal point – a component size, shape, color, or position making it the most important element on the page.
Rule of thirds – it is when dividing an image into thirds.
Harmony – a design where elements balance each other.
Working with clients and what to consider:
Listen to the client.
- Know the market design.
- What is needed for the job.
- Know the budget for the project.
Thumbnails – sketched variations of an idea.
Roughs – a combination of specific elements from each thumbnail.
Comp- show exactly what the final design will look like when printed.
Print proof – used to show indications for folding, cutting, bleeding, trapping, registration or any special requirements for print.
Typography – the study and use of text in a document.
Fair Use Act – a part of the US Copyright law that indicates that excerpts of copyrighted materials may be used under certain circumstances such as news reports, teaching, and research.
Derivative work – it is any work based on one or more works that already exist.
Specifications – refers to a set of documents requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service.
Export – the act of sending or transferring a saved database or element to another application or location.
Gif – Graphic Interchange format (GIF) is a common image file format that has the ability to have frames used in animation.
Graphic – a broad term used to explain objects placed in Indesign such as images.
Hue – a color principle that refers to pure color.
Copyright – a form of protection provided by the laws of the US to authors of ‘original works of authorship’, including, literary, dramatic, musical, artistic, and certain other intellectual works.
Hyperlink – an element on a page that links to another page, webpage, or area on the same page.
Concordant – a typeface that doesn’t have much variety in weight, style, or size.
DPI – Dots Per Inch – refers to the output resolution of a printer or imagesetter.
Process color – is printing using the four standard ink colors; CMYK.
Scaling – is a word that means stretching or shrinking the image to fit a specified area.
Button state – the appearance change of a button when it interacts with a mouse or some other clickable device.
Pixel – so it is the smallest controllable element of a picture represented on the screen.
Cropping – removes certain parts of an image to get a new width and height.
Resampling – changes the number of pixels in an image.
Resizing – resizes or decreases the number of pixels in an image.
Project scope – The work performed to deliver a product, service, or result with the specified features and functions.
Scope – establishes client expectations of which tasks are—and are not—included in the project.
Contrast – This term refers to the differences between design elements, which include color, shape, and scale.
Tint – This color term is created by adding white to a hue.
Shade – This color term is created by adding black to a hue.
White space – This term is sometimes a by-product of proximity, organization, or simplicity.
Baseline shift – a formatting option that moves selected characters above or below the baseline of normal text.
Bounding box – An area that defines the outer border of an object.
Clipboard – The portion of computer memory that holds data that has been cut or copied.
EPS – Encapsulated PostScript – File format used to transfer PostScript data within compatible applications. EPS files can contain text, vector artwork, and images.
Vector graphics – Graphics defined using coordinate points and mathematically drawn lines and curves, which may be freely scaled and rotated without image degradation in the final output.
Typesetting – the arrangement of individual characters of text into words, sentences, or paragraphs.
Trademark – A legal designation that identifies and protects the ownership of a specific device (such as a name, symbol, or mark).
Script font – Typefaces that appear to have been created with a pen or a brush, whether the letters are connected or unconnected.